Try our free PCAT Chemical Processes practice test. We have 48 practice questions with detailed explanations. Great for PCAT Chemistry test prep.
While our foundation has held firm, we pride ourselves on continuing to modernize the curriculum and our teaching practices. The prestigious 2016 Bernard M. Gordon Prize for Innovation in Engineering and Technology Education is a nod both to our history and to our future, recognizing WPI’s project-based curriculum developing leadership

Toggle navigation. Pre-K; garten; 1st Grade; 2nd Grade; 3rd Grade; 4th Grade; Math; Math Games; Math Worksheets; Algebra; Language Arts
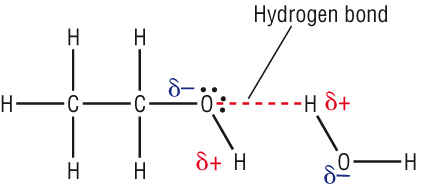
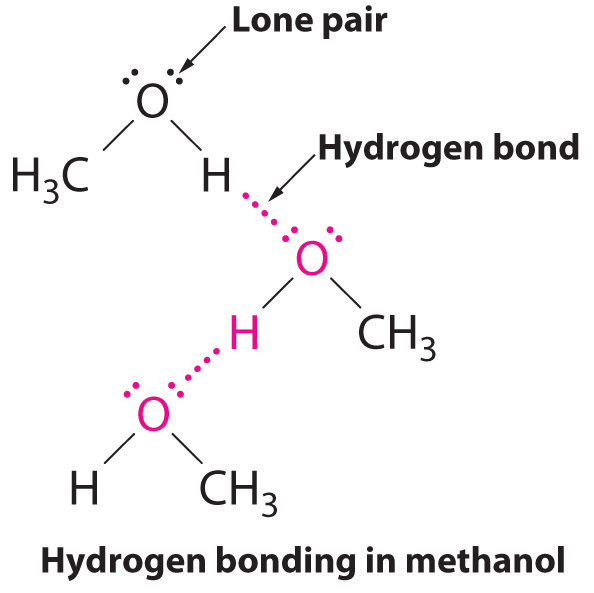
Water has a very high specific heat capacity of 4.1814 J/(g·K) at 25 °C – the second highest among all the heteroatomic species (after ammonia), as well as a high heat of vaporization (40.65 kJ/mol or 2257 kJ/kg at the normal boiling point), both of which are a result of the extensive hydrogen bonding between its molecules.
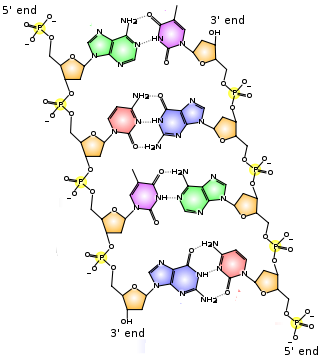
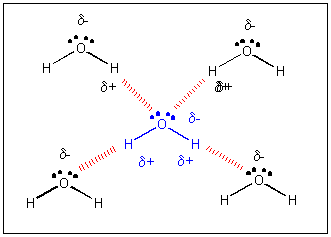
Water (H 2 O, HOH) is the most abundant molecule on Earth’s surface, composing 70-75% of the Earth’s surface as liquid and solid state in addition to being found in the atmosphere as a vapor.
An Introduction to Chemistry. Get started learning about the study of matter. These lecture notes, study guides, lab experiments, and example problems can help you understand the building blocks of life.
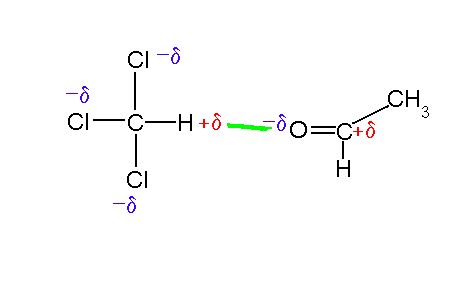
Structure & Bonding. The study of organic chemistry must at some point extend to the molecular level, for the physical and chemical properties of a substance are ultimately explained in terms of the structure and bonding of molecules.


Hydrogen is a chemical element with symbol H and atomic number 1. With a standard atomic weight of 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table.Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
Phosphorous oxychloride | POCl3 or Cl3OP | CID 24813 – structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more.
| Table of Contents | Structure | Williams Home | Molecular Interactions are attractive or repulsive forces between molecules and between non-bonded atoms. Molecular interactions are important in diverse fields of protein folding, drug design, material science, sensors, nanotechnology, separations, and origin of life.